Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Nanjing University, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, National Laboratory of Solid-State Microstructures, Nanjing, China
2 Nanjing University, School of Electronic Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing, China
3 Nanjing University, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Artificial Functional Materials, Nanjing, China
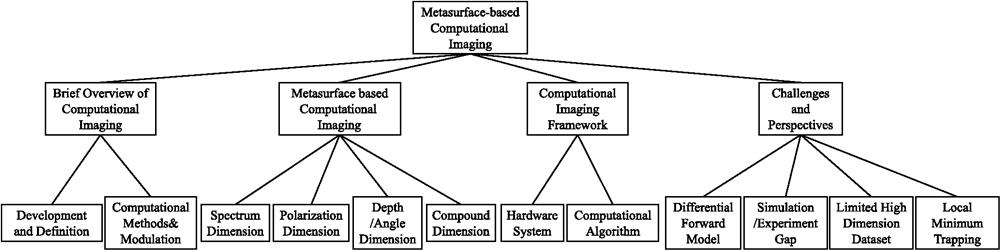
Metasurface-based imaging has attracted considerable attention owing to its compactness, multifunctionality, and subwavelength coding capability. With the integration of computational imaging techniques, researchers have actively explored the extended capabilities of metasurfaces, enabling a wide range of imaging methods. We present an overview of the recent progress in metasurface-based imaging techniques, focusing on the perspective of computational imaging. Specifically, we categorize and review existing metasurface-based imaging into three main groups, including (i) conventional metasurface design employing canonical methods, (ii) computation introduced independently in either the imaging process or postprocessing, and (iii) an end-to-end computation-optimized imaging system based upon metasurfaces. We highlight the advantages and challenges associated with each computational metasurface-based imaging technique and discuss the potential and future prospects of the computational boosted metaimager.
metasurface computational imaging inverse problem algorithm Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(1): 014002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory of Solid-State Microstructures, Key Laboratory of Intelligent Optical Sensing and Integration and College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China.
Achromatic metalens composed of arrays of subwavelength nanostructures with spatially varying geometries is attractive for a number of optical applications. However, the limited degree of freedom in the single layer achromatic metasurface design makes it difficult to simultaneously guarantee the sufficient phase dispersion and high diffraction efficiency, which restricts the achromatic bandwidth and efficiency of metalens. Here we propose and demonstrate a high efficiency achromatic metalens with diffraction-limited focusing capability at the wavelength ranging from 1000 nm to 1700 nm. The metalens comprises two stacked nanopillar metasurfaces, by which the required focusing phase and dispersion compensation can be controlled independently. As a result, in addition to the large achromatic bandwidth, the averaged focusing efficiency of the bilayer metalens is higher than 64% at the near-infrared region. Our design opens up the possibility to obtain the required phase dispersion and efficiency simultaneously, which is of great significance to design broadband metasurface-based optical devices.Achromatic metalens composed of arrays of subwavelength nanostructures with spatially varying geometries is attractive for a number of optical applications. However, the limited degree of freedom in the single layer achromatic metasurface design makes it difficult to simultaneously guarantee the sufficient phase dispersion and high diffraction efficiency, which restricts the achromatic bandwidth and efficiency of metalens. Here we propose and demonstrate a high efficiency achromatic metalens with diffraction-limited focusing capability at the wavelength ranging from 1000 nm to 1700 nm. The metalens comprises two stacked nanopillar metasurfaces, by which the required focusing phase and dispersion compensation can be controlled independently. As a result, in addition to the large achromatic bandwidth, the averaged focusing efficiency of the bilayer metalens is higher than 64% at the near-infrared region. Our design opens up the possibility to obtain the required phase dispersion and efficiency simultaneously, which is of great significance to design broadband metasurface-based optical devices.
metalens metasurface nanostructure waveguide Opto-Electronic Advances
2021, 4(1): 200008
National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences and Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, College of Engineering and Applied Sciences and Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, China
为了满足光码分多址系统中不同用户能够获得不同发送速率的需求,根据所需地址码的容量和码重,通过MATLAB编程,设计出没有重复数字的间隔集,得到具有理想相关性的多码长地址码.根据该地址码的构造特点推导计算出该地址码的误比特率,并绘制出误比特率随同步用户数变化图.设计并仿真了多速率光码分多址系统,分析了误比特率和系统性能.结果表明,该多码长地址码具有良好的相关性和误比特率性能,能够满足各种速率需求的用户.通过系统编解码后能够理想地恢复出原始信号,得到优良的眼图.此研究对光码分多址多速率系统的进一步发展是有帮助的.
光通信 光码分多址 多码长地址码 多速率系统 optical communication optical code division multiple access multi-length address code multi-rate system
广西师范大学电子工程学院, 广西 桂林 541004
以同步二次素数码(SQPC)作为时间扩频序列,单重合序列(OCS)作为波长跳频序列,构造了一种 新的二维光正交码SQPC/OCS,并对其误码性能及码字容量进行了理论分析和仿真比较。理论分析 表明:在同码长、同波长数条件下, SQPC/OCS与 2D-QPC误码率相等,但SQPC/OCS波长数可以是任何数,不局限于素数,从而增加波长码片可以降 低误码率;与扩展素数码 (EPC) EPC/OCS相比,SQPC/OCS误码率更低。SQPC/OCS码字容量远远高于2D-QPC和EPC/OCS码 字容量。仿真结果表明:当p=7、q=13时,SQPC/OCS误码率比2D-QPC降低接近2个数量级;当p=11、 q=15时,SQPC/OCS与EPC/OCS相比,当用户数为20时,误码率相差达4个数量级。
光通信 OCDMA系统 单重合序列 误码率 码容量 optical communication optical code division multiple access system one-coincidence sequence bit error ratio code capacity
在光子晶体环形腔(PCRR)中把原来移除一圈介质柱改为介质柱半径减小,构成环形线缺陷,提出了一种新型的环形腔结构。运用时域有限差分法,分析了光波在环形腔中的传输特性,并进一步讨论了环形线缺陷介质柱半径变化对滤波特性的影响。结果表明,当环形线缺陷介质柱半径选取在0.43R~0.51R 时,可实现单模窄带滤波,中心波长都处于第三通信窗口1550 nm 附近,归一化透射率均在85%以上,脉宽都在17 nm 以下,为波分复用系统中复用/解复用器的设计提供了有价值的参考。
光学器件 光子晶体 环形腔 环形线缺陷 时域有限差分法 波分复用 激光与光电子学进展
2015, 52(1): 012301





